|
|
 发表于 2018-8-9 10:07:08
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 2018-8-9 10:07:08
|
显示全部楼层
本帖最后由 0xCAFEBABE 于 2018-8-9 21:56 编辑
Sarcoma Dataset Coming Soon to Mapping Cancer Markers Project
By: Dr. Igor Jurisica
Krembil Research Institute, University Health Network, Toronto
8 八月 2018
----------
原文及机翻
----------
摘要
In this comprehensive update, the Mapping Cancer Markers team explains how they are determining which genes and gene signatures carry the greatest promise for lung cancer diagnosis. They also introduce the next type of cancer--sarcoma--to be added soon to the project.
在这一全面更新中,映射癌症标记团队解释了他们是如何确定哪些基因和基因签名对肺癌诊断具有最大的希望。他们还介绍了下一种癌症——肉瘤——即将加入该项目。
The Mapping Cancer Markers (MCM) project continues to process work units for the ovarian cancer dataset. As we accumulate these outcomes, we continue to analyze MCM results from the lung cancer dataset. In this update, we discuss preliminary findings from this analysis. In addition, we introduce the sarcoma dataset that will be our focus in the next stage.
映射癌症标记物(MCM)项目继续处理卵巢癌数据集的工作单位。当我们积累这些结果时,我们继续分析肺癌数据集的MCM结果。在本次更新中,我们将讨论初步分析结果。此外,我们介绍了肉瘤数据集,将是我们在下一个阶段的重点。
Patterns of gene-family biomarkers in lung cancer
肺癌基因家族生物标志物的模式
In cancer, and human biology in general, multiple groups of biomarkers (genes, protein, microRNAs, etc.) can have similar patterns of activity and thus clinical utility, helping diagnosis, prognosis or predicting treatment outcome. For each cancer subtype, one could find large number of such groups of biomarkers, each having similar predictive power; yet current statistical and AI-based methods identify only one from a given data set.
在癌症和人类生物学中,多组生物标志物(基因、蛋白质、microRNA等)可以具有类似的活动模式,从而具有临床实用性,有助于诊断、预后或预测治疗结果。对于每个癌症亚型,人们可以发现大量这样的生物标志物,每个都具有相似的预测能力;然而,目前的统计和基于人工智能的方法仅从给定的数据集中识别出一个。
We have two primary goals in MCM: 1) to find good groups of biomarkers for the cancers we study, and 2) to identify how and why these biomarkers form useful groups, so we can build a heuristic approach that will find such groups for any disease without needing months of computation on World Community Grid. The first goal will give us not only information that after validation may be useful in clinical practice, but importantly, it will generate data that we will use to validate our heuristics.
我们在MCM中有两个主要目标:1)寻找我们研究的癌症的良好生物标记组,和2)识别这些生物标记如何以及为什么形成有用的组,因此我们可以构建一种启发式方法,可以在不需要数个月的世界通信计算的情况下为任何疾病找到这样的组。TY网格。第一个目标将不仅给我们信息,验证后可能是有用的在临床实践中,但重要的是,它将产生的数据,我们将用于验证我们的启发式。
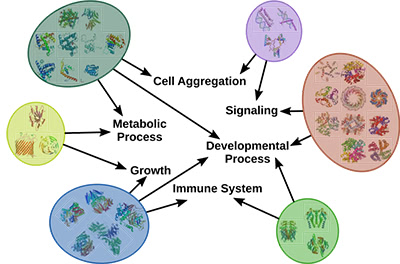
Illustration 1: Proteins group by similar interactions and similar biological functions.
图解1:蛋白质组由相似的相互作用和相似的生物学功能组成。
Multiple groups of biomarkers exist primarily due to the redundancy and complex wiring of the biological system. For example, the highly interconnected human protein-protein interaction network enables us to see how individual proteins perform diverse molecular functions and together contribute to a specific biological process, as shown above in Illustration 1. Many of these interactions change between healthy and disease states, which in turn affects the functions these proteins carry. Through these analyses, we aim to build models of these processes that in turn could be used to design new therapeutic approaches.
多组生物标记物的存在主要是由于生物系统的冗余和复杂的布线。例如,高度相互连接的人蛋白-蛋白质相互作用网络使我们能够看到个体蛋白质如何执行不同的分子功能并共同促成特定的生物过程,如上文在图1中所示。许多这些相互作用在健康状态和疾病状态之间变化,进而影响这些蛋白质携带的功能。通过这些分析,我们的目标是建立这些过程的模型,进而可以用来设计新的治疗方法。
Two specific groups of biomarkers may appear different from each other, yet perform equivalently because the proteins perform similar molecular functions. However, using these groups of biomarkers for patient stratification may not be straightforward. Groups of biomarkers often do not validate in new patient cohorts or when measured by different biological assays, and there are thousands of possible combinations to consider. Some groups of biomarkers may have all reagents available while others may need to be develop (or be more expensive); they may also have different robustness, sensitivity and accuracy, affecting their potential as clinically useful biomarkers.
生物标志物的两个特定基团可能会出现彼此不同,但等效地执行,因为蛋白质执行类似的分子功能。然而,使用这些生物标志物对患者分层可能并不简单。生物标志物的组通常不验证在新的患者队列中或当通过不同的生物测定来测量,并且有成千上万种可能的组合要考虑。一些生物标志物可能有所有试剂可用,而其他一些可能需要开发(或更昂贵);它们也可能具有不同的健壮性、敏感性和准确性,影响它们作为临床有用生物标志物的潜力。
At the present time, there is no effective approach to find all good groups of biomarkers necessary to achieve the defined goal, such as accurately predicting patient risk or response to treatment.
目前,还没有有效的方法来找到所有必要的生物标志物来实现所定义的目标,例如准确预测患者的风险或对治疗的反应。
The first goal of the Mapping Cancer Markers project is to gain a deeper understanding of the “rules” of why and how proteins interact and can be combined to form a group of biomarkers, which is essential to understanding their role and applicability. Therefore, we are using the unique computational resource of World Community Grid to systematically survey the landscape of useful groups of biomarkers for multiple cancers and purposes (diagnosis and prognosis). Thereby, we established a benchmark for cancer gene biomarker identification and validation. Simultaneously, we are applying unsupervised learning methods such as hierarchical clustering to proteins that group by predictive power and biological function.
癌症标记物项目的第一个目标是深入了解蛋白质相互作用的原因和规律,并将它们组合起来形成一组生物标记物,这对于了解它们的作用和适用性是至关重要的。因此,我们利用世界社区网格的独特计算资源,系统地调查多种癌症和目的(诊断和预后)的有用生物标记群的景观。因此,我们建立了一个癌症基因标志物鉴定和验证的基准。同时,我们采用无监督学习方法,如分层聚类的蛋白质组的预测能力和生物功能。
The combination of this clustering and the World Community Grid patterns enables us to identify generalized gene clusters that provide deeper insights to the molecular background of cancers, and give rise to more reliable groups of gene biomarkers for cancer detection and prognosis.
这种集群和世界社区网格模式的结合使我们能够识别广义的基因簇,从而为癌症的分子背景提供更深入的见解,并为癌症检测和预后提供更可靠的基因生物标记组。
Currently, we are focusing on the first-phase results from the lung cancer dataset, which focused on a systematic exploration of the entire space of potential fixed-length groups of biomarkers.
目前,我们关注的是肺癌数据集的第一阶段结果,其重点是对潜在固定长度的生物标志物的整个空间的系统探索。
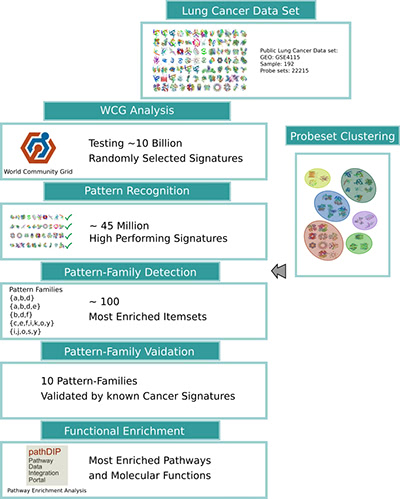
Illustration 2: Workflow of the MCM-gene-pattern-family search. The results of the World Community Grid analysis combined with the unsupervised clustering of genes identifies a set of gene-pattern-families, generalizing the groups of biomarkers. Finally, the results are evaluated using known cancer biomarkers and by using functional annotations, such as signaling pathways, gene ontology function and processes.
说明2:MCM基因模式家族搜索的流程。世界社区网格分析与基因的无监督聚类结合的结果识别了一组基因模式家族,概括了生物标志物的组。最后,使用已知的癌症生物标志物和使用功能注释,如信号通路、基因本体功能和过程来评价结果。
As depicted above in Illustration 2, World Community Grid computed about 10 billion randomly selected groups of biomarkers, to help us understand the distribution of which group sizes and biomarker combinations perform well, which in turn we will use to validate heuristic approaches. Analysis showed that about 45 million groups of biomarkers had a high predictive power and passed the quality threshold. This evaluation gives us a detailed and systematic picture of which genes and gene groups carry the most valuable information for lung cancer diagnosis. Adding pathway and protein interaction network data enables us to further interpret and fathom how and why these groups of biomarkers perform well, and what processes and functions these proteins carry.
如图2所示,世界社区网格计算了100亿个随机选择的生物标记组,以帮助我们了解哪些组大小和生物标记组合的分布表现良好,这反过来我们将用于验证启发式方法。分析表明,约4500万组生物标志物具有较高的预测能力,并通过了质量阈值。这个评价给我们一个详细和系统的图片,哪些基因和基因组携带最有价值的信息为肺癌诊断。添加途径和蛋白质相互作用网络数据使我们能够进一步解释和揣测这些生物标记物如何以及为什么表现良好,以及这些蛋白质携带哪些过程和功能。
Simultaneously, we used the described lung cancer data to discover groups of similar genes. We assume that these genes or the encoded proteins fulfill similar biological functions or are involved in the same molecular processes.
同时,我们使用所描述的肺癌数据来发现相似基因的组。我们假设这些基因或编码的蛋白质实现相似的生物学功能或参与相同的分子过程。
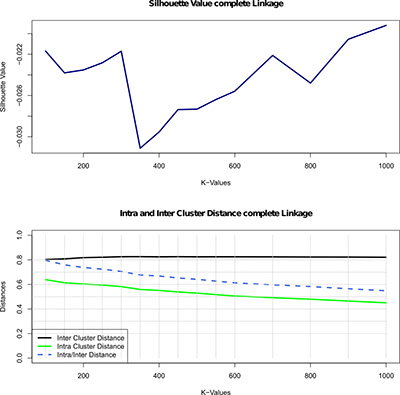
Illustration 3: Evaluation of the hierarchical clustering of the lung cancer data, using the complete linkage parameter, for different numbers of groups indicated by the K-values (100 to 1000). The first plot shows the silhouette value - a quality metric in this clustering, i.e., measure of how well each object relates to its cluster compared to other clusters. The second plot depicts the inter- and intra-cluster distance and the ratio of intra/inter cluster distance.
说明3:使用完整的连锁参数对K值(100至1000)所指示的不同数目的组的肺癌数据的分级聚类进行评价。第一个情节显示剪影值-在这个聚类中的质量度量,即,衡量每个对象相对于它的集群与其他集群相比有多好。第二个图描绘了簇内距离和簇内距离以及簇内/簇间距离的比率。
To find the appropriate clustering algorithms and the right number of gene groups (clusters) we use different measures to evaluate the quality of each of the individual clustering. For instance, Illustration 3 (above) shows the results of the evaluation of the hierarchical clustering for different numbers of clusters. To evaluate clustering quality, we used silhouette value (method for assessing consistency within clusters of data, i.e., measure of how well each object relates to its own cluster compared to other clusters). A high silhouette value indicates good clustering configuration, and the figure shows a large increase in the silhouette value at 700 gene groups. Since this indicates a significant increase in quality, we subsequently select this clustering for further analysis.
为了找到合适的聚类算法和正确数量的基因群(簇),我们使用不同的措施来评估每个个体聚类的质量。例如,图解3(上文)示出了对于不同数量的簇的层次聚类的评价结果。为了评估聚类质量,我们使用轮廓值(用于评估数据簇内的一致性的方法,即,衡量每个对象相对于它自己的集群与其他集群相比有多好)。一个高的轮廓值表明良好的聚类配置,并且图显示在700个基因组中剪影值的大幅增加。由于这表明质量的显著提高,我们随后选择这种聚类进行进一步的分析。
Not all combinations of biological functions or the lack of it will lead to cancer development and will be biologically important. In the next step, we apply a statistical search to investigate which combinations of clusters are most common among the well-preforming biomarkers, and therefore result in gene groups or pattern families. Since some gene-pattern-families are likely to occur even at random, we use enrichment analysis to ensure the selection only contains families that occur significantly more often than random.
不是所有生物功能的组合或缺乏它都会导致癌症的发展,并且在生物学上是重要的。在下一个步骤中,我们应用统计搜索来研究哪些簇合物在预形成的生物标志物中最常见,从而导致基因组或模式家族。由于一些基因模式家族甚至可能随机出现,所以我们使用富集分析来确保选择只包含显著多于随机发生的家庭。
In the subsequent step we validated the selected generalized gene-pattern-families using an independent set of 28 lung cancer data sets. Each of these studies report one or several groups of biomarkers of up- or down-regulated genes that are indicative for lung cancer.
在随后的步骤中,我们使用一组独立的28个肺癌数据集验证选定的广义基因模式家族。这些研究报告了一种或几组生物标志物,它们是肺癌的上调或下调基因。
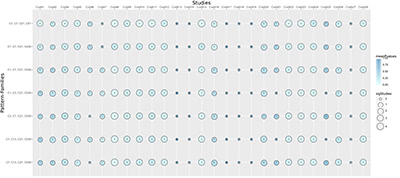
Illustration 4: Shown is a selection of high performing pattern families and how they are supported by 28 previously published gene signatures. Each circle in the figure indicates the strength of the support: The size of the circle represents the number of clusters in the family that where found significantly more often in the signature of this study. The color of the circle indicates the average significance calculated for all clusters in the pattern-family.
插图4:示出了高性能模式家族的选择以及它们如何被28个先前公布的基因签名所支持。图中的每个圆表示支持的强度:圆的大小代表家庭中的簇的数目,在这项研究的签名中发现了更多的簇。圆的颜色表示模式族中所有簇计算的平均值。
Illustration 4 depicts a selection of the most prevalent pattern families and the studies that support them. Each circle in the figure indicates the strength of the support: The size of the circle represents the number of clusters in the family that where found significantly more often in the biomarker of this study. The color of the circle indicates the average significance calculated for all clusters in the pattern-family.
插图4:示出了高性能模式家族的选择以及它们如何被28个先前公布的基因签名所支持。图中的每个圆表示支持的强度:圆的大小代表家庭中的簇的数目,在这项研究的签名中发现了更多的簇。圆的颜色表示模式族中所有簇计算的平均值。
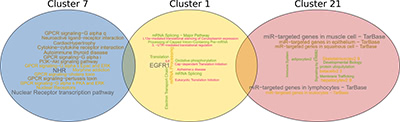
Illustration 5: One of the most frequent gene-pattern-families, is a combination of cluster 1, 7 and 21. We annotated each cluster with pathways using pathDIP and visualized it using word clouds (the larger the word/phrase, the most frequently it occurs).
插图5:最常见的基因模式家族之一,是簇1, 7和21的组合。我们用PATDIP注释每个簇的路径,并用词云可视化它(单词/短语越大,出现的频率越大)。
Finally, we annotated the most effective gene-pattern-families and their gene clusters with molecular functions and pathways that the genes or corresponding proteins are involved in. Illustration 5 shows an example for such a gene-pattern-family that comprises gene-clusters 7, 1 and 21.
最后,我们用基因或相应的蛋白参与的分子功能和途径来注释最有效的基因型家族及其基因簇。图解5示出了包括基因簇7, 1和21的这样的基因模式家族的示例。
The word cloud visualization indicates that cluster 7 is involved in pathways related to GPCRs (G protein–coupled receptor) and NHRs (nuclear hormone receptors). In contrast, the genes in cluster 1 are highly enriched in EGFR1 (epidermal growth factor receptor) as well as translational regulation pathways. Mutations affecting the expression of EGFR1, a transmembrane protein, have shown to result in different types of cancer, and in particular lung cancer (as we have shown earlier, e.g., (Petschnigg et al., J Mol Biol 2017; Petschnigg et al., Nat Methods 2014)). The aberrations increase the kinase activity of EGFR1, leading to hyperactivation of downstream pro-survival signaling pathways and a subsequent uncontrolled cell division. The discovery of EGFR1 initiated the development of therapeutic approaches against various cancer types including lung cancer. The third group of genes are common targets of microRNAs. Cluster 21 indicates strong involvement with microRNAs, as we and others have shown before (Tokar et al., Oncotarget 2018; Becker-Santos et al., J Pathology, 2016; Cinegaglia et al., Oncotarget 2016).
云可视化表明,簇7参与了与GPCRs(G蛋白偶联受体)和NHRs(核激素受体)相关的通路。相反,簇1中的基因高度富集EGFR1(表皮生长因子受体)和翻译调控途径。影响EGFR1,跨膜蛋白的表达的突变已经显示出不同类型的癌症,特别是肺癌(如我们先前所示,例如,(Pet Snigigg等人,J.mol BioL 2017;PeStHigigg等人,NAT方法2014))。畸变增加EGFR1的激酶活性,导致下游的促存活信号通路的过度激活和随后的不受控制的细胞分裂。EGFR1的发现引发了针对各种癌症类型的治疗方法的发展,包括肺癌。第三组基因是microRNA的共同靶点。集群21表明与microRNA的强烈参与,正如我们和其他人之前所展示的(Tokar等人,OnCo Talk 2018;Becker Santos等人,J病理学,2016;CieGigaLa等人,OnCo Talk 2016)。
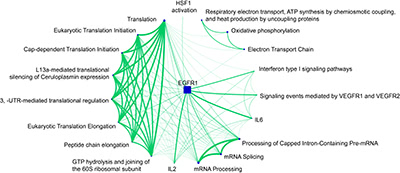
Illustration 6: Evaluation of enriched pathways for cluster 1. Here we used our publicly available pathway enrichment analysis portal pathDIP (Rahmati et al., NAR 2017). The network was generated with our network visualization and analysis tool NAViGaTOR 3 (http://ophid.utoronto.ca/navigator).
图解6:簇1的富集途径的评价。在这里,我们使用我们的公开途径富集分析门户PATDIP(RaMaTaI等人,NAR 2017)。该网络是由我们的网络可视化和分析工具 NAViGaTOR 3 生成的。
The final illustration evaluates the 20 most significantly enriched pathways for cluster 1. The size of the pathway nodes corresponds to the number of involved genes, and the width of the edges corresponds the number genes of overlapping between pathways. One can see that all pathways involved in translation are highly overlapping. mRNA-related pathways form another highly connected component in the graph. The EGFR1 pathway is strongly overlapping with many of the other pathways, indicating that genes that are affected by those pathways are involved in a similar molecular mechanism.
最后的图解评估了群集1的20个最显著富集的途径。路径节点的大小对应于所涉及的基因的数量,并且边缘的宽度对应于路径之间重叠的数量基因。可以看出,翻译中涉及的所有途径都是高度重叠的。mRNA相关通路在图中形成另一高度连接的组分。EGFR1通路与许多其它途径强重叠,表明受这些途径影响的基因参与了类似的分子机制。
Sarcoma
肉瘤
After lung and ovarian cancers, next we will focus on sarcoma. Sarcomas are a heterogeneous group of malignant tumors that are relatively rare. They are typically categorized according to the morphology and type of connective tissues that they arise in, including fat, muscle, blood vessels, deep skin tissues, nerves, bones and cartilage, which comprises less than 10% of all malignancies (Jain 2010). Sarcomas can occur anywhere in the human body, from head to foot, can develop in patients of any age including children, and often vary in aggressiveness, even within the same organ or tissue subtype (Honore 2015). This suggests that a histological description by organ and tissue type is neither sufficient for categorization of the disease nor does it help in selecting the most optimal treatment.
在肺癌和卵巢癌之后,接下来我们将关注肉瘤。肉瘤是一组罕见的恶性肿瘤。它们通常根据它们所产生的结缔组织的形态和类型来分类,包括脂肪、肌肉、血管、深部皮肤组织、神经、骨骼和软骨,其中包括不到10%的所有恶性肿瘤(JAIN 2010)。肉瘤可以发生在人体的任何地方,从头到脚,可以在任何年龄的儿童中发展,并且经常在攻击性上变化,即使在相同的器官或组织亚型(HONER 2015)中。这表明器官和组织类型的组织学描述既不足以分类疾病,也不利于选择最理想的治疗方法。
Diagnosing sarcomas poses a particular dilemma, not only due to their rarity, but also due to their diversity, with more than 70 histological subtypes, and our insufficient understanding of the molecular characteristics of these subtypes (Jain 2010).
诊断肉瘤提出了一个特殊的困境,不仅由于其稀有,但也由于其多样性,超过70个组织亚型,我们对这些亚型的分子特征的理解不足(JAIN 2010)。
Therefore, recent research studies focused on molecular classifications of sarcomas based on genetic alterations, such as fusion genes or oncogenic mutations. While research achieved major developments in local control/limb salvage, the survival rate for “high-risk” soft tissue sarcomas (STSs) has not improved significantly, especially in patients with a large, deep, high-grade sarcoma (stage III) (Kane III 2018).
因此,最近的研究集中在肉瘤的分子分类的基础上,如融合基因或致癌突变的遗传改变。虽然研究取得了重大进展,局部控制/保肢,“高风险”软组织肉瘤(STSS)的生存率并没有得到显著改善,尤其是在大,深,高级别肉瘤患者(III期)(Kane III 2018)。
For these reasons, in the next phase of World Community Grid analysis, we will focus on the evaluation of the genomic background of sarcoma. We will utilize different sequencing information and technologies to gain a broader knowledge between the different levels of genetic aberrations and the regulational implications. We will provide a more detailed description of the data and the incentives in the next update.
由于这些原因,在下一阶段的世界社区网格分析中,我们将着重于对肉瘤基因组背景的评估。我们将利用不同的测序信息和技术,以获得更广泛的知识之间的不同水平的遗传变异和调节的含义。我们将在下一次更新中提供数据和激励的更详细的描述。
- Petschnigg J, Kotlyar M, Blair L, Jurisica I, Stagljar I, and Ketteler R, Systematic identification of oncogenic EGFR interaction partners, J Mol Biol, 429(2): 280-294, 2017.
- Petschnigg, J., Groisman, B., Kotlyar, M., Taipale, M., Zheng, Y., Kurat, C., Sayad, A., Sierra, J., Mattiazzi Usaj, M., Snider, J., Nachman, A., Krykbaeva, I., Tsao, M.S., Moffat, J., Pawson, T., Lindquist, S., Jurisica, I., Stagljar, I. Mammalian Membrane Two-Hybrid assay (MaMTH): a novel split-ubiquitin two-hybrid tool for functional investigation of signaling pathways in human cells; Nat Methods, 11(5):585-92, 2014.
- Rahmati, S., Abovsky, M., Pastrello, C., Jurisica, I. pathDIP: An annotated resource for known and predicted human gene-pathway associations and pathway enrichment analysis. Nucl Acids Res, 45(D1): D419-D426, 2017.
- Kane, John M., et al. "Correlation of High-Risk Soft Tissue Sarcoma Biomarker Expression Patterns with Outcome following Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation." Sarcoma 2018 (2018).
- Jain, Shilpa, et al. "Molecular classification of soft tissue sarcomas and its clinical applications." International journal of clinical and experimental pathology 3.4 (2010): 416.
- Honore, C., et al. "Soft tissue sarcoma in France in 2015: epidemiology, classification and organization of clinical care." Journal of visceral surgery 152.4 (2015): 223-230.
- Tokar T, Pastrello C, Ramnarine VR, Zhu CQ, Craddock KJ, Pikor L, Vucic EA, Vary S, Shepherd FA, Tsao MS, Lam WL, Jurisica Differentially expressed microRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma invert effects of copy number aberrations of prognostic genes. Oncotarget. 9(10):9137-9155, 2018
- Becker-Santos, D.D., Thu, K.L, English, J.C., Pikor, L.A., Chari, R., Lonergan, K.M., Martinez, V.D., Zhang, M., Vucic, E.A., Luk, M.T.Y., Carraro, A., Korbelik, J., Piga, D., Lhomme, N.M., Tsay, M.J., Yee, J., MacAulay, C.E., Lockwood, W.W., Robinson, W.P., Jurisica, I., Lam, W.L., Developmental transcription factor NFIB is a putative target of oncofetal miRNAs and is associated with tumour aggressiveness in lung adenocarcinoma, J Pathology, 240(2):161-72, 2016.
- Cinegaglia, N.C., Andrade, S.C.S., Tokar, T., Pinheiro, M., Severino, F. E., Oliveira, R. A., Hasimoto, E. N., Cataneo, D. C., Cataneo, A.J.M., Defaveri, J., Souza, C.P., Marques, M.M.C, Carvalho, R. F., Coutinho, L.L., Gross, J.L., Rogatto, S.R., Lam, W.L., Jurisica, I., Reis, P.P. Integrative transcriptome analysis identifies deregulated microRNA-transcription factor networks in lung, adenocarcinoma, Oncotarget, 7(20): 28920-34, 2016.
Other news
其他新闻
We have secured a major funding from Ontario Government for our research: The Next Generation Signalling Biology Platform. The main goal of the project is developing novel integrated analytical platform and workflow for precision medicine. This project will create an internationally accessible resource that unifies different types of biological data, including personal health information—unlocking its full potential and making it more usable for research across the health continuum: from genes and proteins to pathways, drugs and humans.
我们已经获得了安大略政府为我们的研究提供的主要资金:下一代信号生物学平台。该项目的主要目标是开发新的精密医疗分析平台和工作流程。该项目将创建一个国际可访问的资源,统一不同类型的生物数据,包括个人健康信息解锁其全部潜力,并使其更适用于跨健康连续性的研究:从基因和蛋白质到通路、药物和HU。曼斯。
We have also published papers describing several tools, portals and applications with our collaborators. Below we list those most related directly or indirectly to work on World Community Grid:
我们也发表了一些描述我们合作者的工具、门户和应用的论文。下面我们直接或间接地列出那些与世界社区网格相关的工作:
- Wong, S., Pastrello, C., Kotlyar, M., Faloutsos, C., Jurisica, I. SDREGION: Fast spotting of changing communities in biological networks. ACM KDD Proceedings, 2018. In press. BMC Cancer, 18(1):408, 2018.
- Kotlyar, M., Pastrello, C., Rossos, A., Jurisica, I. Protein-protein interaction databases. Eds. Cannataro, M. et al. Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, 81, Elsevier. In press. doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811414-8.20495-1
- Rahmati, S., Pastrello, C., Rossos, A., Jurisica, I. Two Decades of Biological Pathway Databases: Results and Challenges, Eds. Cannataro, M. et al. Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, 81, Elsevier. In press.
- Hauschild, AC, Pastrello, C., Rossos, A., Jurisica, I. Visualization of Biomedical Networks, Eds. Cannataro, M. et al. Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, 81, Elsevier. In press.
- Sivade Dumousseau M, Alonso-López D, Ammari M, Bradley G, Campbell NH, Ceol A, Cesareni G, Combe C, De Las Rivas J, Del-Toro N, Heimbach J, Hermjakob H, Jurisica I, Koch M, Licata L, Lovering RC, Lynn DJ, Meldal BHM, Micklem G, Panni S, Porras P, Ricard-Blum S, Roechert B, Salwinski L, Shrivastava A, Sullivan J, Thierry-Mieg N, Yehudi Y, Van Roey K, Orchard S. Encompassing new use cases - level 3.0 of the HUPO-PSI format for molecular interactions. BMC Bioinformatics, 19(1):134, 2018.
- Minatel BC, Martinez VD, Ng KW, Sage AP, Tokar T, Marshall EA, Anderson C, Enfield KSS, Stewart GL, Reis PP, Jurisica I, Lam WL., Large-scale discovery of previously undetected microRNAs specific to human liver. Hum Genomics, 12(1):16, 2018.
- Tokar T, Pastrello C, Ramnarine VR, Zhu CQ, Craddock KJ, Pikor L, Vucic EA, Vary S, Shepherd FA, Tsao MS, Lam WL, Jurisica, I. Differentially expressed microRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma invert effects of copy number aberrations of prognostic genes. Oncotarget. 9(10):9137-9155, 2018.
- Paulitti A, Corallo D, Andreuzzi E, Bizzotto D, Marastoni S, Pellicani R, Tarticchio G, Pastrello C, Jurisica I, Ligresti G, Bucciotti F, Doliana R, Colladel R, Braghetta P, Di Silvestre A, Bressan G, Colombatti A, Bonaldo P, Mongiat M. Matricellular EMILIN2 protein ablation ca 1 uses defective vascularization due to impaired EGFR-dependent IL-8 production, Oncogene, Feb 27. doi: 10.1038/s41388-017-0107-x. [Epub ahead of print] 2018.
- Tokar, T., Pastrello, C., Rossos, A., Abovsky, M., Hauschild, A.C., Tsay, M., Lu, R., Jurisica. I. mirDIP 4.1 – Integrative database of human microRNA target predictions, Nucl Acids Res, D1(46): D360-D370, 2018.
- Kotlyar M., Pastrello, C., Rossos, A., Jurisica, I., Prediction of protein-protein interactions, Current Protocols in Bioinf, 60, 8.2.1–8.2.14., 2017.
- Singh, M., Venugopal, C., Tokar, T., Brown, K.B., McFarlane, N., Bakhshinyan, D., Vijayakumar, T., Manoranjan, B., Mahendram, S., Vora, P., Qazi, M., Dhillon, M., Tong, A., Durrer, K., Murty, N., Hallet, R., Hassell, J.A., Kaplan, D., Jurisica, I., Cutz, J-C., Moffat, J., Singh, D.K., RNAi screen identifies essential regulators of human brain metastasis initiating cells, Acta Neuropathologica, 134(6):923-940, 2017.
Thank you
致谢
This work would not be possible without the participation of World Community Grid Members. Thank you for generously contributing CPU cycles, and for your interest in this and other World Community Grid projects.
没有世界社区网格成员的参与,这项工作是不可能进行的。感谢您慷慨贡献CPU周期,以及您对这个和其他世界社区网格项目的兴趣。
=========
那啥,上面是机翻哈,可能有诸多不正确的地方,等大神来指点。
----------
大意
----------
当前阶段是收集卵巢癌的数据,并继续分析肺癌的数据。
下一种癌症——肉瘤——即将加入该项目,作为下一个阶段的重点。
|
评分
-
查看全部评分
|