Distnibuted Computing Team ChinaInformation in Chinese 1.Discuss the reason 21 years, the world's largest distributed computing SETI
@home The search for the alien project is terminated.SETI@home Officially, the project will enter hibernation from March 31, 2020, and volunteer computing resources distributed around the world will no longer receive new packets.Then we volunteers can't stop, So how will we explore the extraterrestrial civilization?I think we should explore ourselves, at least for a whileBut self exploration here means that small groups of distributed computing screen planets and organize them.And the power of distributed computing, I think it is necessary to give another example.“At the turn of the century, decentralized protocols, such as email and Usenet, led distributed computing projects, such as SETI@Home and Folding@Home ; And peer-to-peer applications such as Napster, BitTorrent, and tor. Sean Parker was one of the founders of Napster and later the CEO of Facebook.From 1990 to 2003, more than 20 organizations around the world contributed to the human genome project, mapping the entire human genome. Critics predict that the task could take 100 years or more. However, by sharing data sets and computing resources, and by accelerating technological innovation, the project was completed in only 13 years.”【quote:Author: Eric Elliott Eric Elliott is the author of writing software and writing JavaScript applications. He is also co-founder of Eric elliottjs.com and devonywhere.】 2. The idea of planets and the value of screening“The necessary condition for life is the source of energy (usually solar energy, but not all). But it is usually when many other conditions, such as the planet's geophysics, geochemistry and astrophysics, are ripe that the planet will be called habitable. The existence of extraterrestrial life is still unknown. The habitability of planets is based on the environment of the solar system and the earth to speculate whether other stars will be suitable for life. Planets with high habitability are usually those with persistent and complex multicellular and unicellular life systems. The research and theory of planetary habitability is an integral part of astroscience, and is becoming a new subject of astrobiology.The necessary condition for life is the source of energy (usually solar energy, but not all). But it is usually when many other conditions, such as the planet's geophysics, geochemistry and astrophysics, are ripe that the planet will be called habitable. The existence of extraterrestrial life is still unknown. The habitability of planets is based on the environment of the solar system and the earth to speculate whether other stars will be suitable for life. Planets with high habitability are usually those with persistent and complex multicellular and unicellular life systems. The research and theory of planetary habitability is an integral part of astroscience, and is becoming a new subject of astrobiology.’”It can be seen from these literatures that there are many planets that can be screened, and the application prospect is very high, and the research value is also very high.Take the case I know about myself. Because I don't have the funds and there are not so many conditions, so I have been relying on the extrasolar star map, Simbad and care insu to screen the planets with Univer site, ICSU and other institutional systems. As a result, I feel the feasibility of planetary screening more intuitively.Because I don't have the funds and there are not so many conditions, so I have been relying on the extrasolar star map, Simbad and care insu to screen the planets with Univer site, ICSU and other institutional systems. As a result, I feel the feasibility of planetary screening more intuitively.conditionCalculation method: About livable zoneThe proportion of the relationship between the mass and luminosity of stars in the main sequence phase is that the luminosity of stars is directly proportional to the 3-4 power growth of the mass, while the lifetime is inversely proportional to the 2-3 power equation of the mass! In the concept of habitable zone, distance is a very important concept, because the light radiation received by the planet is inversely proportional to the square distance of the planet's orbit![ See the figure below]
〈F3〉
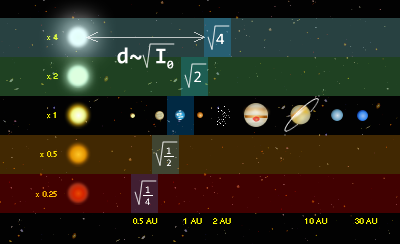
Habitable zone (astronomical unit) l = √ target celestial luminosity / stellar luminositySpectral type“The spectral type of a star represents the photosphere temperature of the star and is related to its mass. The possible spectrum types of habitable stars range from f or G at medium temperature to k at low temperature, that is, from 7000K to about 4000K. The sun is one of them, which belongs to G2 type. Most stars similar to the sun can provide high habitability for the planets around them. Stars with this condition must exist for at least billions of years, so that life can have a chance to reproduce on the planets around them. Bright main sequence stars of type O, B and a usually exist for less than a billion years, and some only exist for less than 10 million years.In addition, stars with this condition will release enough high-energy ultraviolet light to make the planets around them start the atmospheric movement, such as the formation of the ozone layer, but at the same time, there should not be too many ionization reactions to kill the newborn life.A planet with high habitability will travel far away from its star, which can prevent the liquid water on the surface of the planet from dissipating due to tidal lock-in.These stars should be moderate in temperature, not too hot or too cold, and should exist for a long time, so that there is a chance of life. About five to ten percent of the stars in the Milky way, where the solar system is located, belong to this type. However, whether the dim K and M-type stars (such as red dwarfs) can provide the living environment for the planets around them is a hot topic recently, because it is traditionally believed that only the planets with main sequence stars have the opportunity to provide the living environment. This issue will be discussed in more detail below.Habitable zoneHabitable zones are planets that orbit stars and have liquid water on their surfaces. In addition to energy sources, liquid water is regarded as the most important thing for life, just like life on earth. If you include those that don't need water to support life (such as liquid ammonia), the number of habitable planets will increase dramatically.A stable habitable zone has two characteristics. First, this belt cannot be greatly changed. All stars will increase their brightness as they age, and their habitable areas will adjust outward. However, if this happens too quickly, such as a super huge star, the planets around the star will be more difficult to provide an environment for life. The calculation method of planet habitability is never simple, and it will be affected by many factors. In order to calculate the planet's habitability, the atmospheric conditions and geological needs of the observed planet are assumed. Whether this assumption is correct or not greatly affects the accuracy of the calculation. In fact, even when we calculate the habitability of the sun's planets, there are great fluctuations.Second, it is not allowed to have massive objects close to this area, because it will affect the composition of such earth planets. Suppose that if Jupiter orbits between the earth and Venus, neither will appear. Previous astronomers thought that the inner planets in the solar system are solid planets, while the outer planets are gas planets, which is quite normal. However, the discovery of the outer planets in the solar system changed this idea. Countless Jupiter like planets in other galaxies operate in areas considered habitable. However, it is often easier to observe Jupiter like planets in the outer solar system, so it is not clear which is normal.Low brightness conversionThe luminosity change of stars is very common, but its range is very large. Most stars are very stable, but a few important stars often suddenly increase brightness and release a lot of energy. Because of their instability, such stars are considered unable to provide the living environment for the planets around them. Obviously, ordinary living things can't survive with great temperature changes. The luminosity instability may also be caused by the lethal gamma and X-rays emitted by the star itself. If a planet has an atmosphere, its impact can be minimized, but the protection is limited, so planets that are heavily exposed to these rays are usually not suitable for living beings.The sun is very special. The difference between the maximum and minimum luminosity is one thousandth in eleven solar cycles. There is clear evidence that even a very small amount of solar brightness change will greatly affect the earth's climate. The little ice age of the last millennium (1500-1800) may have been the result of a brief decrease in the brightness of the sun. Therefore, other stars do not need to have obvious brightness changes, which may also affect the habitability of the planets around them.Highly metallic featuresAlthough stars are mainly composed of hydrogen and helium, they also contain other heavy metals, and the contents are not the same. The stars with high heavy metal content are usually directly related to the heavy metal content in the protoplanetary disk. Less heavy metal in the protoplanetary disk makes it less likely to form planets around stars, according to the theory of solar nebulae at the edge of the solar system. If any planet lacks metal, its mass will be lower and it will become a Jupiter like planet, which is not suitable for living things. The study of spectroscopy points out that in the planets of the outer solar system, if the main star has no companion star, the planet itself can obtain more metal composition, which has a better chance to form earth like planets, and the possibility of life will be higher.”The above literature simply describes the necessary factors for the screening of livable zone, and we deduce them by ourselves. There are loopholes in this screening.First, suppose that aliens need exactly the same living conditions as the earth; Second, even if there is such a hypothesis, other environments may also create areas suitable for life outside the aforementioned habitable zone[Quoted from Evolution of aliens by Ian Stewart and Jack Cohen].Different forms of life can be found in different environments. It is too conservative to expose these limited hypotheses.So let's just talk about ordinary carbon based life:In a planetary system, it is believed that planets must be in habitable zones for life to occur. In concept, the habitable zone of the disk around a star is a spherical shell like space surrounded by a star. The surface temperature of all planets in the range should be able to keep water liquid. Liquid water is considered to be vital to life because it is used as a solvent for biochemical reactions. In 1959, physicists Philip Morrison and Giuseppe coconi mentioned such areas in their research papers on the search for extraterrestrial civilization. In 1961, Frank Drake made this concept known by Drake equation.The distance between the habitable zone and the star can be calculated by the luminosity of the star. For selected stars, the range of distances can be determined by the following equation:
〈F4〉
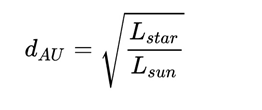
Here It's the habitable zone distance in astronomical units,L star It's the radiant calorific value of a star.L sun It's the radiant calorific value of the sun.For example, a star with a luminosity of 25% of the sun has a habitable zone distance of about 0.5 Au, while a star with a luminosity of twice that of the sun has a habitable zone distance of about 1.4 Au. This is because the luminosity follows the inverse square law. Assuming (especially) that it has a similar atmospheric structure and thickness to the earth, and the distance between the center of the habitable zone of the exoplanets and the parent star, it must have a global average temperature environment similar to the earth.When a star becomes brighter and its luminosity increases due to evolution, the habitable zone around the disk will move outward with time. The maximum time that organisms can exist is that the longer a planet's orbit stays in the habitable zone, the better.The composition of the atmosphere also has an important impact. The temperature of the planet is affected by the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.The basic theory of planetary screening is over.summary[As for distributed computing algorithm, I'm not very good at it.] I think single scheduler can be used. Single scheduler has resource information of all nodes, and tasks are distributed by single scheduler, so it has a global view and can control the overall resources more accurately.The state synchronization of single scheduling system is relatively easy and stable, because the state of resource usage and task execution is managed uniformly, which reduces the difficulty of state synchronization and concurrency control.I propose that during the period of the suspension of the plan, we can switch to planetary screening.Methods we can use Drake's method and the habitable zone proposed by Philip Morrison and Giuseppe kokoni in the paper, and use resources and distributed computing to analyze the atmosphere and other necessary factors (references).The report is over.24-25 may 2021 (concluded on 25 April)